

- #Git clone command username password how to#
- #Git clone command username password install#
- #Git clone command username password password#
You can save, or cache, your credentials so that you don't have to reenter them each time you interact with the remote repository.
#Git clone command username password password#
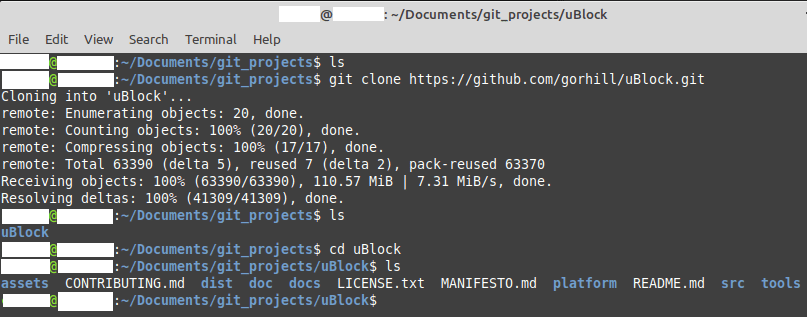
Saving your password or token to avoid entering it If you're just interacting with repositories, you probably want to simply select 'repo' as the "scope". You can create a token using these instructions or simply go here. One good option is to use a personal authentication token in place of a password. You'll be asked to enter your username and password (where the latter could be either your GitHub password or your personal authentication token).Īs of fall 2021, GitHub will no longer allow usage of a password alone. You can clone a repository using HTTPS like this: git clone The standard way to interact with a repository is via HTTPS. Using HTTPS with a personal authentication token or a password In what follows, I'll refer to the account or organization the repository exists in as ACCOUNT and the repository as REPO. With either of the first two approaches you can avoid entering a username and password each time you interact with the remote repository, as discussed below.īefore going into details, note that you can run the following (generally run from a directory within a repository) to see how things are configured: git config -l Using your GitHub password with 2-factor authentication.Using a personal authentication token or password.There are three main approaches you can take: This documentation focuses on GitHub but the ideas are relevant for other platforms. Git provides multiple protocols for authenticating to and interacting with remote Git repositories.
#Git clone command username password how to#
This documentation outlines how to connect to remote Git repositories, in particular how to avoid entering a password or authentication token each time. Berkeley Statistics Annual Research Symposium (BSTARS).Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning.You're new to Git, you might also want to review the information in Where can I learn more about Git? and Getting started with Git and AWS CodeCommit. To learn how to create and push your first commit, see Create a commit in AWS CodeCommit.
Follow the steps in Getting started with CodeCommit to start using CodeCommit. For more informationĪbout Git and how it manages credentials, see Credentialįor more information, see Connect to the CodeCommit repository by cloning the repository and Create a commit.
#Git clone command username password install#
If you do not have a credential store or credential management utilityĬonfigured on your local computer, you can install one. Should not be prompted again unless you change the password, inactivate the GitĬredentials, or delete the Git credentials in IAM. Saved for you in a credential store or credential management utility. Password generated for Git credentials in IAM (the ones you created in Step 3: Create Git credentials for HTTPS connections to CodeCommit).ĭepending on your operating system and other software, this information might be Included in Git for Windows), your IDE, or Git itself. Manager utility for your version of Git (for example, the Git Credential Manager Depending on the configuration of your localĬomputer, this prompt either originates from a credential management system The first time you connect, you are prompted for the user name and To install Git, we recommend websites such as Git Downloads. We recommend using a recent version of Git.

Git version 2.28 supports configuring the branch name for initial commits. CodeCommit supports Git versions 1.7.9 and later. To work with files, commits, and other information in CodeCommit repositories, you must install For more information, seeĬommand line reference. If you want to use AWS CLI commands with CodeCommit, install the AWS CLI. If theįor more information about CodeCommit managed policies and sharing access to repositories with other groups and users, see Share a repositoryĪnd Authentication and access control for Review to review the list of policies to attach to the IAM user. For more information, see AWS managed policies forĪfter you have selected the policy you want to attach, choose Next: In Grant permissions, choose Attach existing policiesįrom the list of policies, select AWSCodeCommitPowerUser or another On the Permissions tab, choose Add Permissions. In the IAM console, in the navigation pane, choose Users, and then choose the IAM user you want to configure for CodeCommit access. Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the IAM console at. For more information, see AWS KMS and encryption. If you are using an existing IAM user, make sure there are no policies attached to the user that expressly deny the AWS KMS actions requiredīy CodeCommit. CodeCommit requires AWS Key Management Service.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
